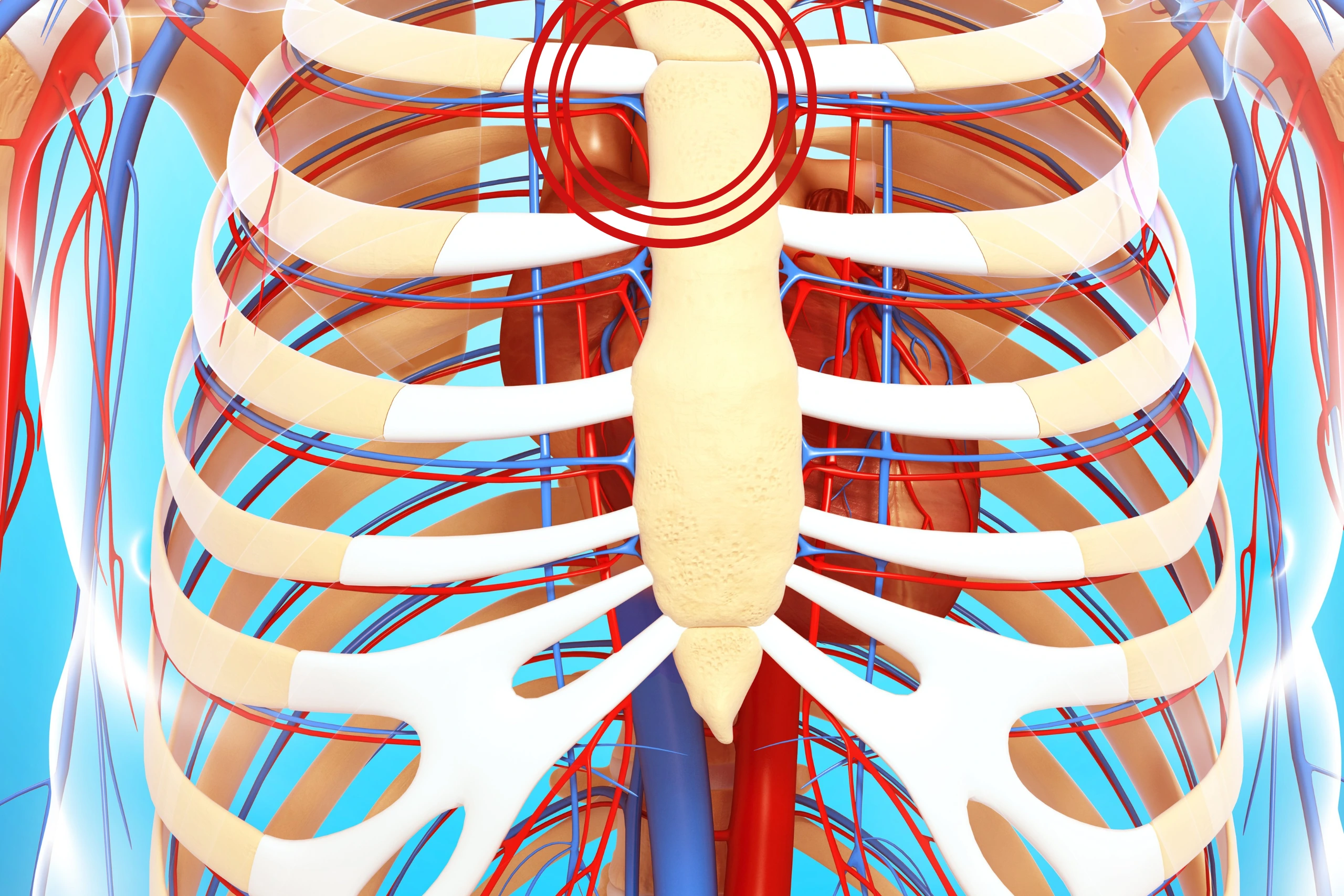
Understanding Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries
The sternoclavicular joint (SCJ) is a unique joint that connects the sternum (breastbone) to the clavicle (collarbone) and plays a crucial role in stabilizing the upper extremity and supporting various shoulder movements. While relatively rare, injuries to the SCJ can occur due to trauma, overuse, or degenerative conditions. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for musculoskeletal Sternoclavicular Joint injuries to help you better understand this complex joint and the management of related injuries.
Before discussing SCJ injuries, let’s briefly review the anatomy and function of the joint. The SCJ is a synovial joint that allows movement in multiple planes, facilitating shoulder girdle motion. Ligaments and surrounding muscles help stabilize the joint, preventing excessive movement and potential dislocation.
Causes of Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries
Injuries to the SCJ can result from various causes, including:
a) Trauma: A direct blow to the front of the shoulder or a fall onto an outstretched hand can cause SCJ injuries. Car accidents, sports-related collisions, and contact sports are common scenarios for traumatic injuries.
b) Overuse or Repetitive Motion: Repetitive overhead activities or improper shoulder mechanics can lead to chronic strain and inflammation of the SCJ, resulting in overuse injuries.
c) Degenerative Conditions: In some cases, degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis can affect the SCJ, leading to gradual joint damage and pain.
Symptoms of SC Joint Injuries
Symptoms of SCJ injuries can vary based on the severity and underlying cause. Common signs and symptoms include:
a) Pain: Pain at the SCJ is the most prominent symptom. The pain may be localized to the joint area or radiate to the shoulder, neck, or arm.
b) Swelling: Inflammation and swelling can occur around the SCJ due to soft tissue damage.
c) Limited Range of Motion: SCJ injuries can restrict shoulder movements, making it difficult to lift the arm or perform certain activities.
d) Tenderness: The joint area may be tender to touch, indicating local inflammation.
e) Clicking or Popping Sensations: Some individuals may experience clicking or popping sensations during shoulder movements.
f) Dislocation: Severe injuries can result in SCJ dislocation, which is characterized by visible deformity and an inability to move the joint.
Types of Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries
- Sprains and Strains: Mild injuries that involve stretching or tearing of the ligaments or muscles around the SCJ.
- Dislocations: Partial or complete displacement of the clavicle from the sternum due to trauma or significant force.
- Arthritis: Degenerative changes in the SCJ, leading to joint inflammation, pain, and limited mobility.
Diagnosing Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries
Proper diagnosis of SCJ injuries is essential to initiate appropriate treatment. Diagnosis often involves a combination of:
- Physical Examination: The healthcare provider will assess the joint area for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be ordered to visualize the joint and assess the extent of the injury.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound may be used to evaluate soft tissue damage, especially in cases of strains and sprains.
Treatment Options for SC Joint Injuries
The treatment approach for SCJ injuries depends on the severity and type of injury. Conservative treatments are often recommended for mild to moderate injuries, while severe cases may require surgical intervention. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Immobilization: Resting the affected arm and immobilizing the shoulder with a sling or brace helps reduce stress on the SCJ, promoting healing.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications or prescribed analgesics can alleviate pain and inflammation, under medical supervision.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic Care plays a vital role in restoring joint function, strengthening surrounding muscles, and improving range of motion.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce swelling and inflammation, while heat can relax muscles and promote blood flow during the healing process.
- Joint Aspiration: In cases of SCJ arthritis with significant inflammation, joint aspiration may be performed to relieve fluid buildup and alleviate pain.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases of SCJ dislocations or fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve realigning the joint, stabilizing the clavicle, or repairing damaged ligaments or tendons.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery: Recovery from SCJ injuries can take several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the injury and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment. Rehabilitation programs are essential for regaining full joint function, strength, and mobility.
Prevention of SC Joint Injures:
While some SCJ injuries are unavoidable, certain preventive measures can reduce the risk of injury:
- Proper technique and body mechanics during sports and physical activities.
- Strengthening exercises for the shoulder and upper body muscles.
- Gradual progression of exercise intensity and duration to prevent overuse injuries.
Sternoclavicular Joint injuries, though relatively uncommon, can cause significant pain and discomfort, affecting shoulder movement and overall quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for effective management and successful recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for SCJ injuries, individuals can seek timely medical attention and work closely with healthcare providers to regain optimal shoulder function and prevent future injuries.